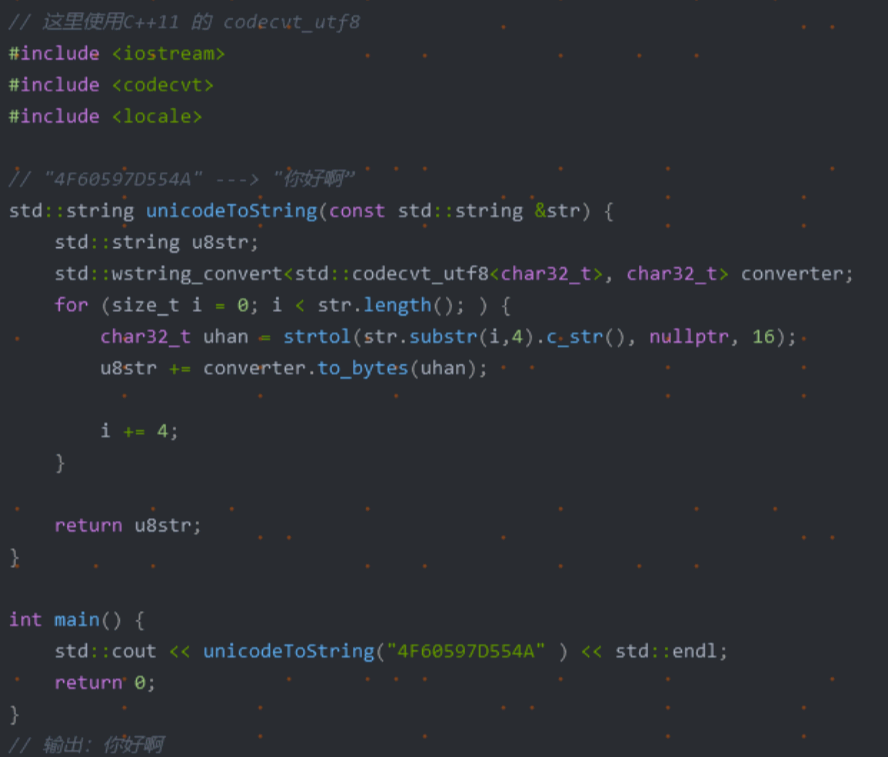
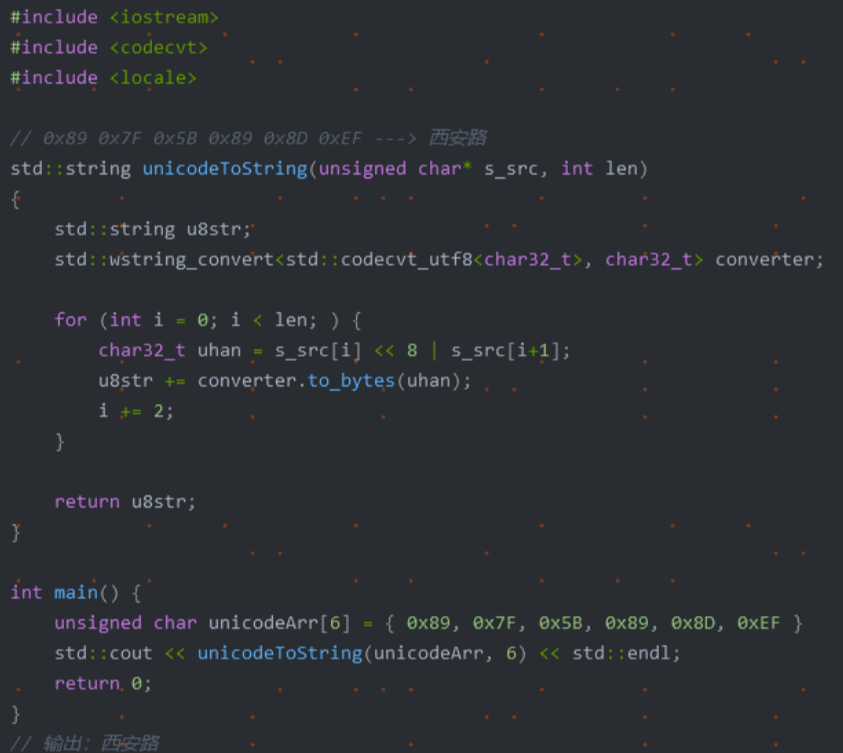
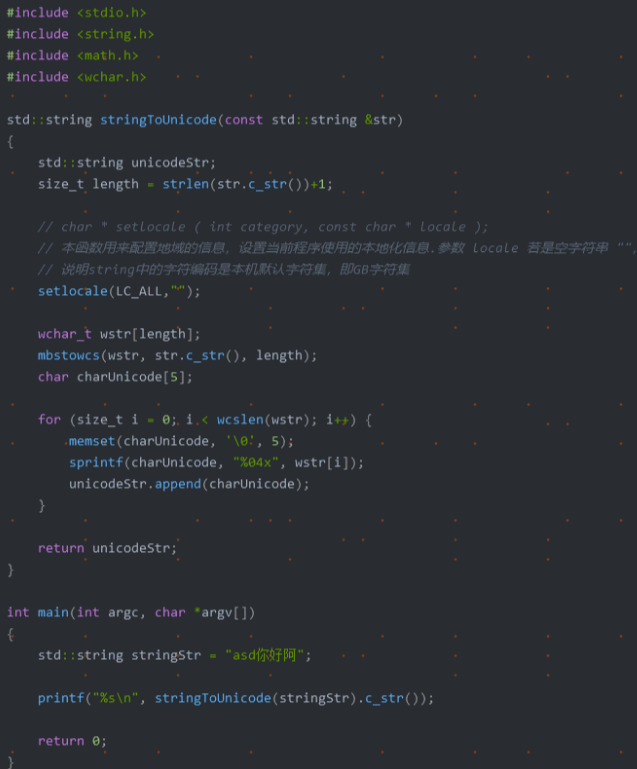
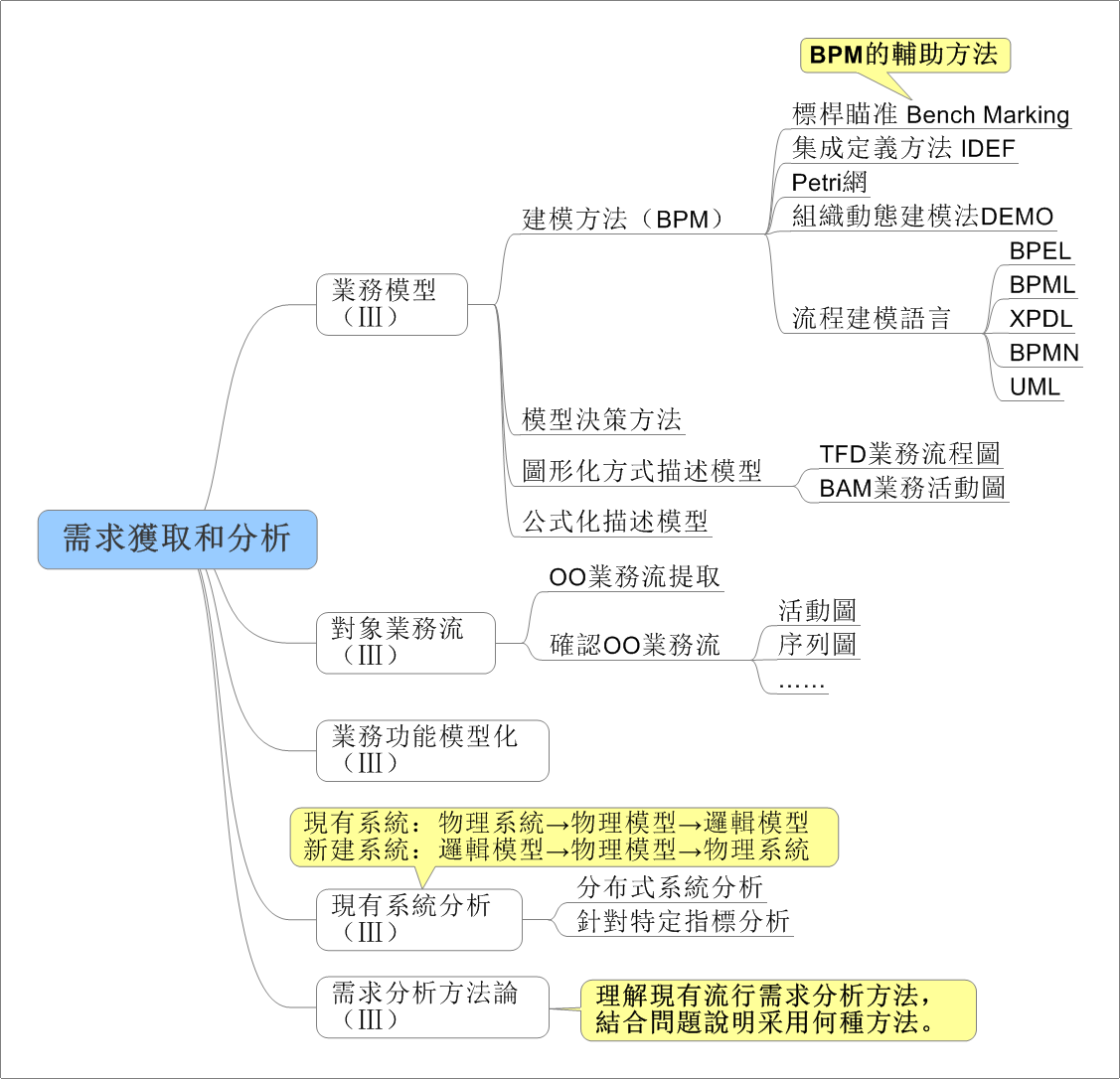
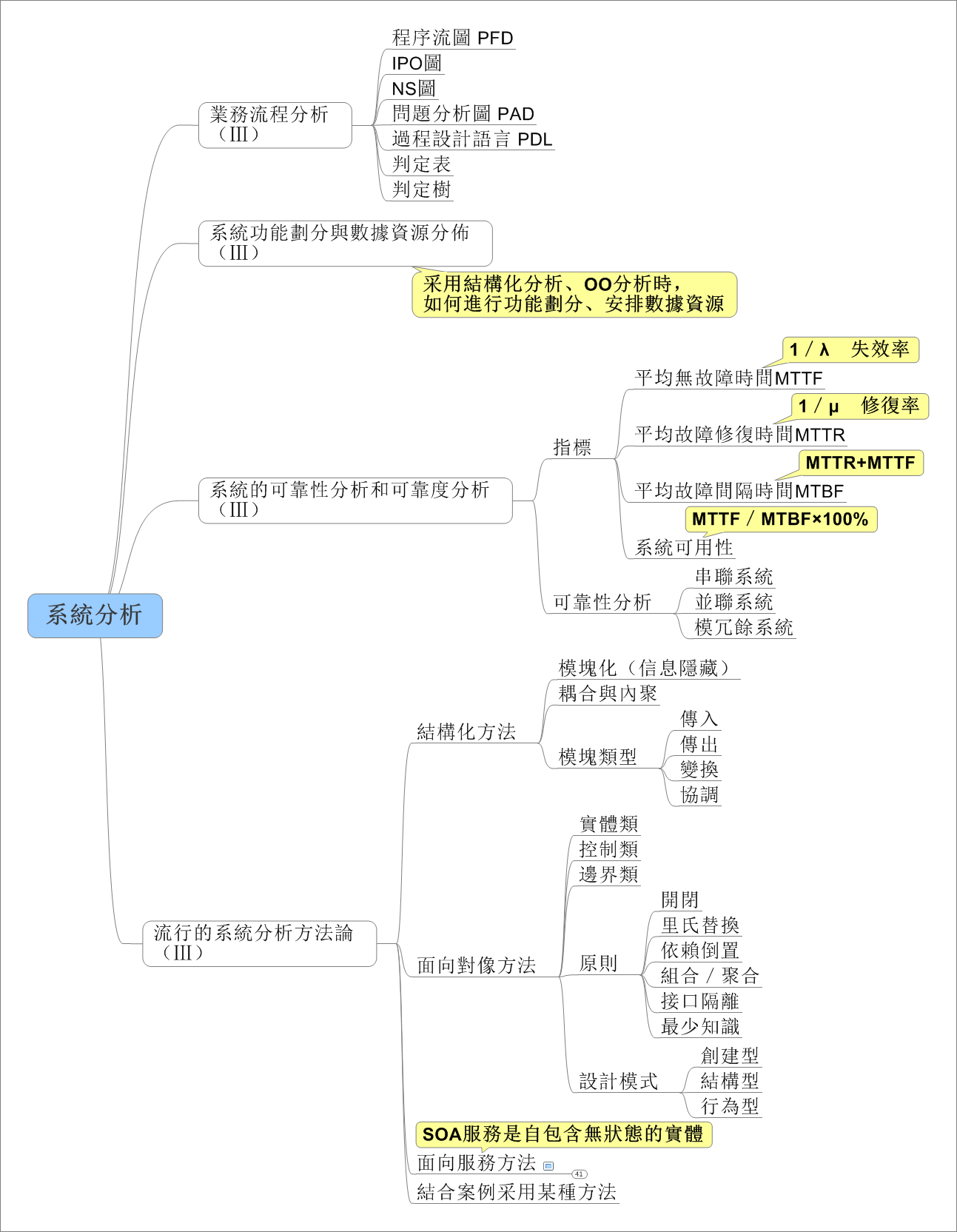
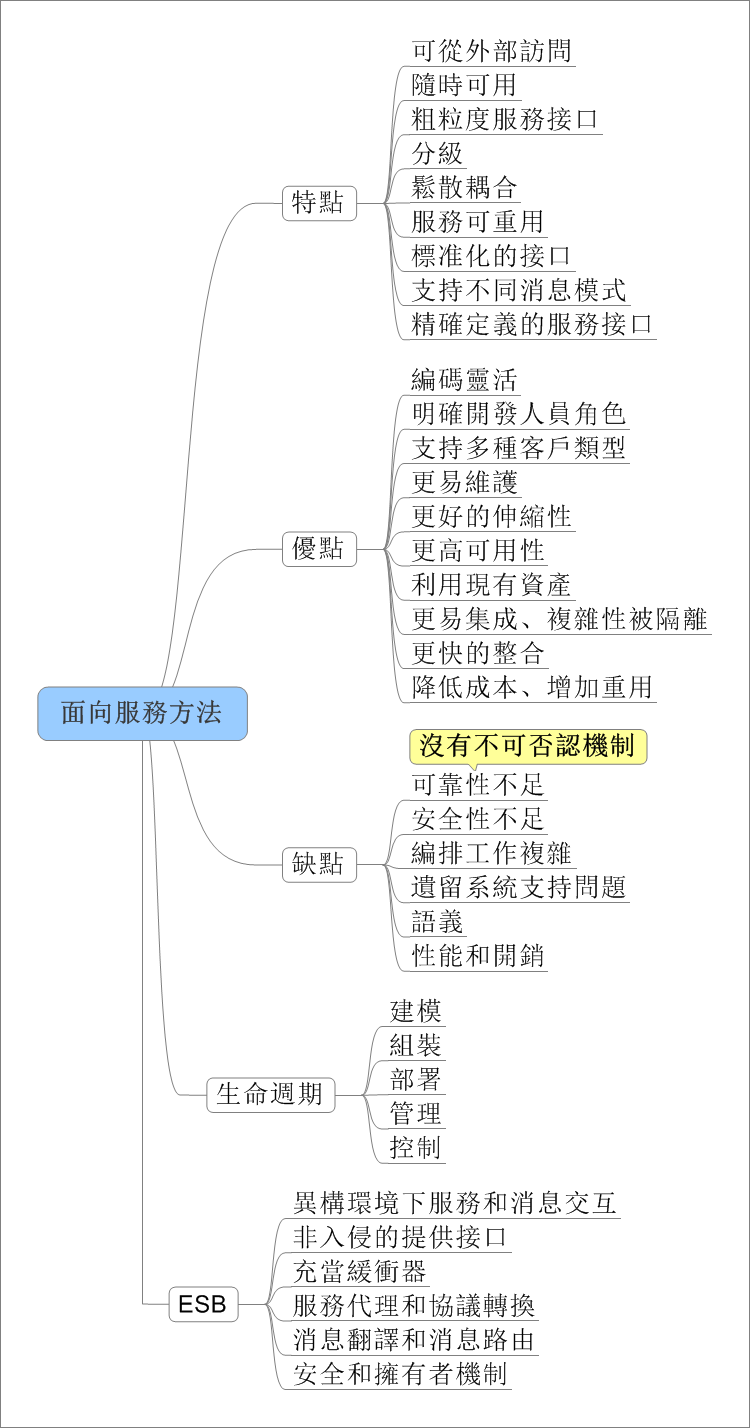
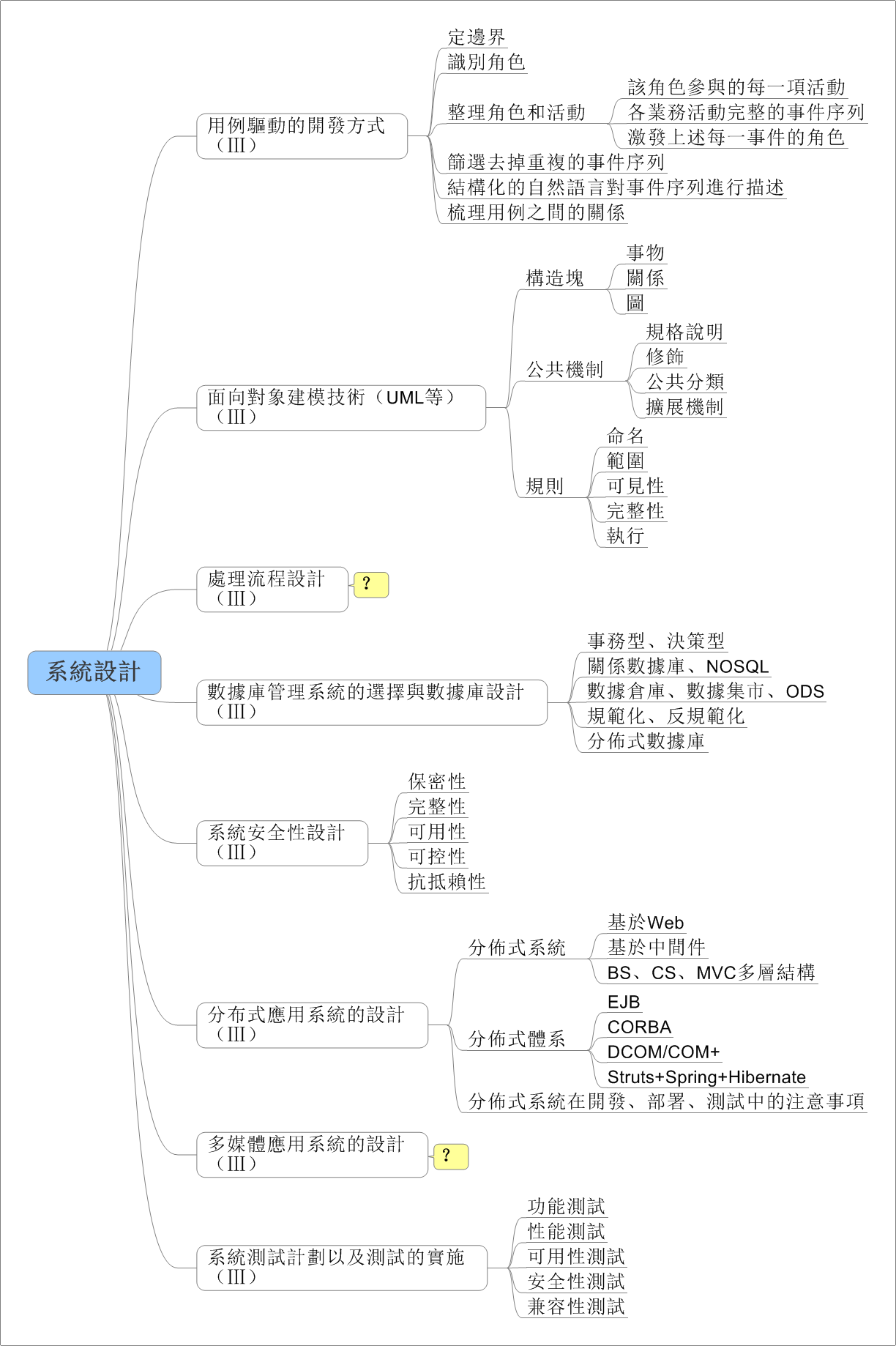
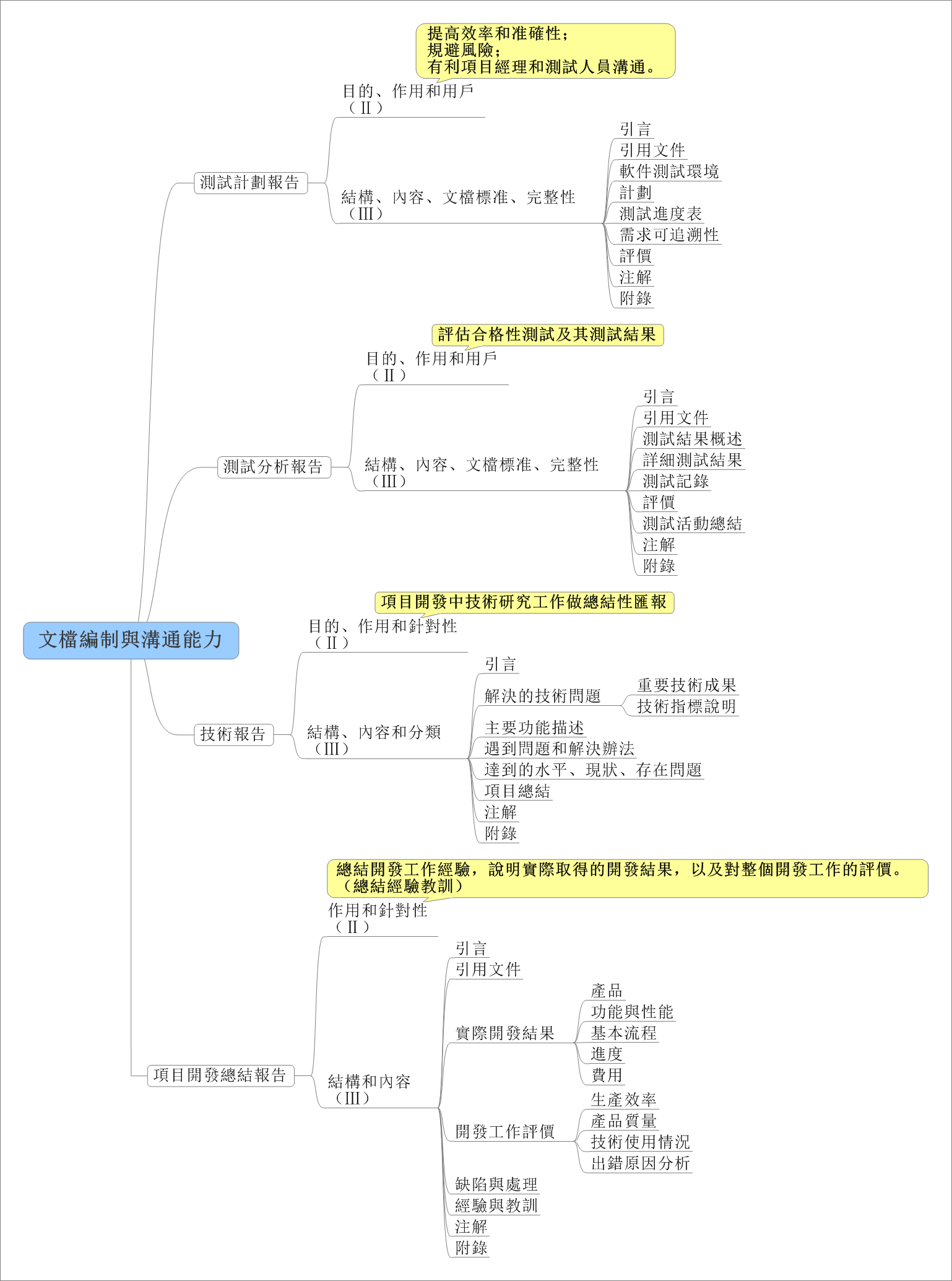
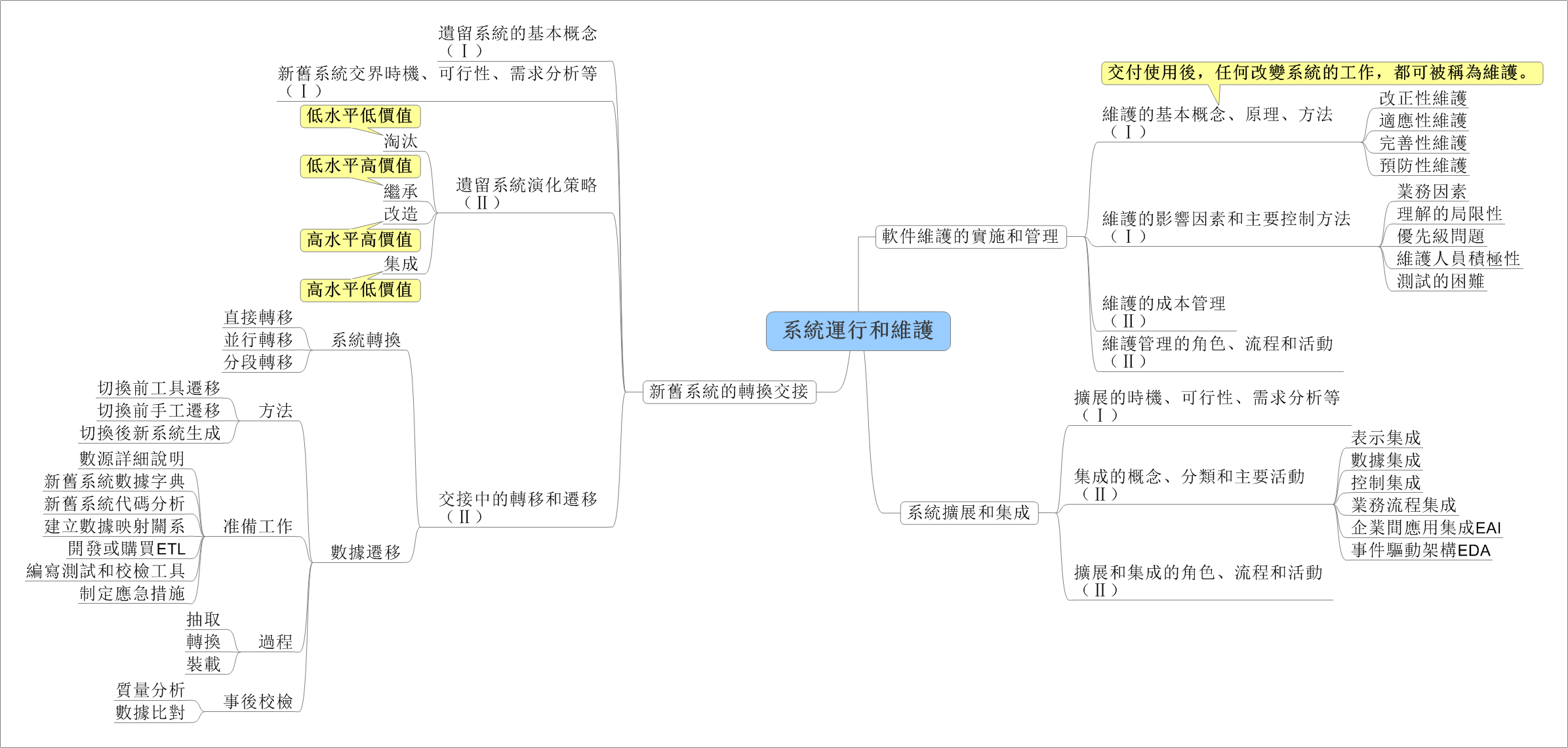
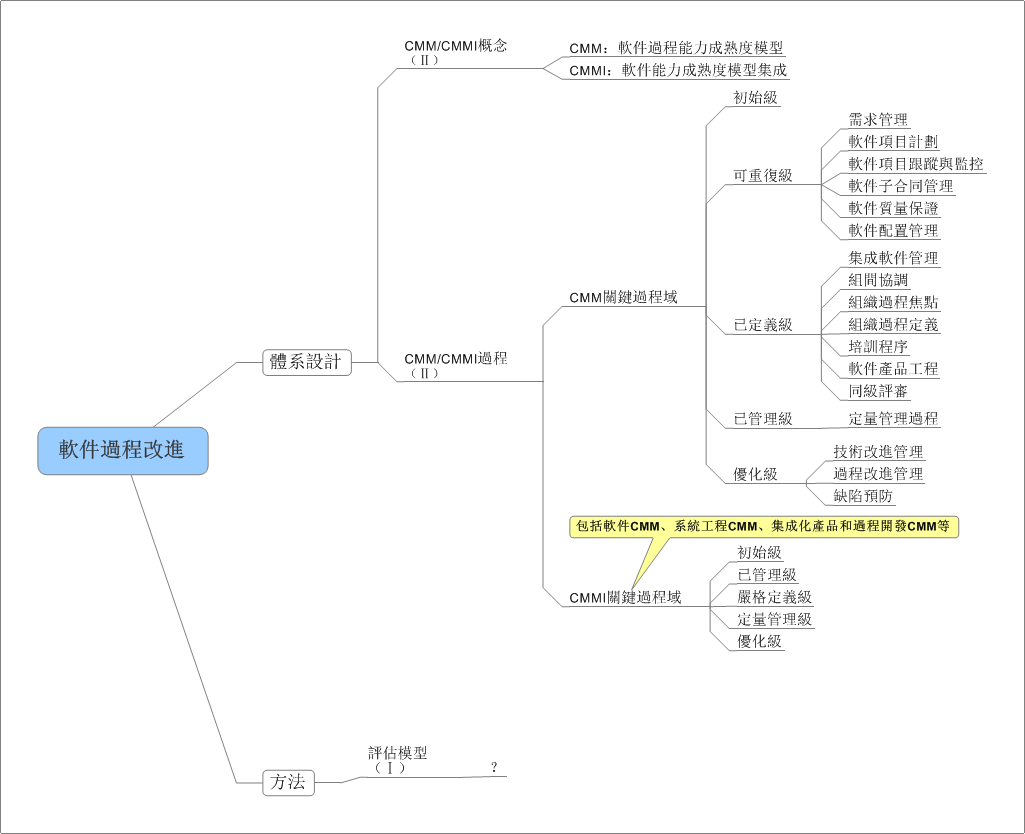
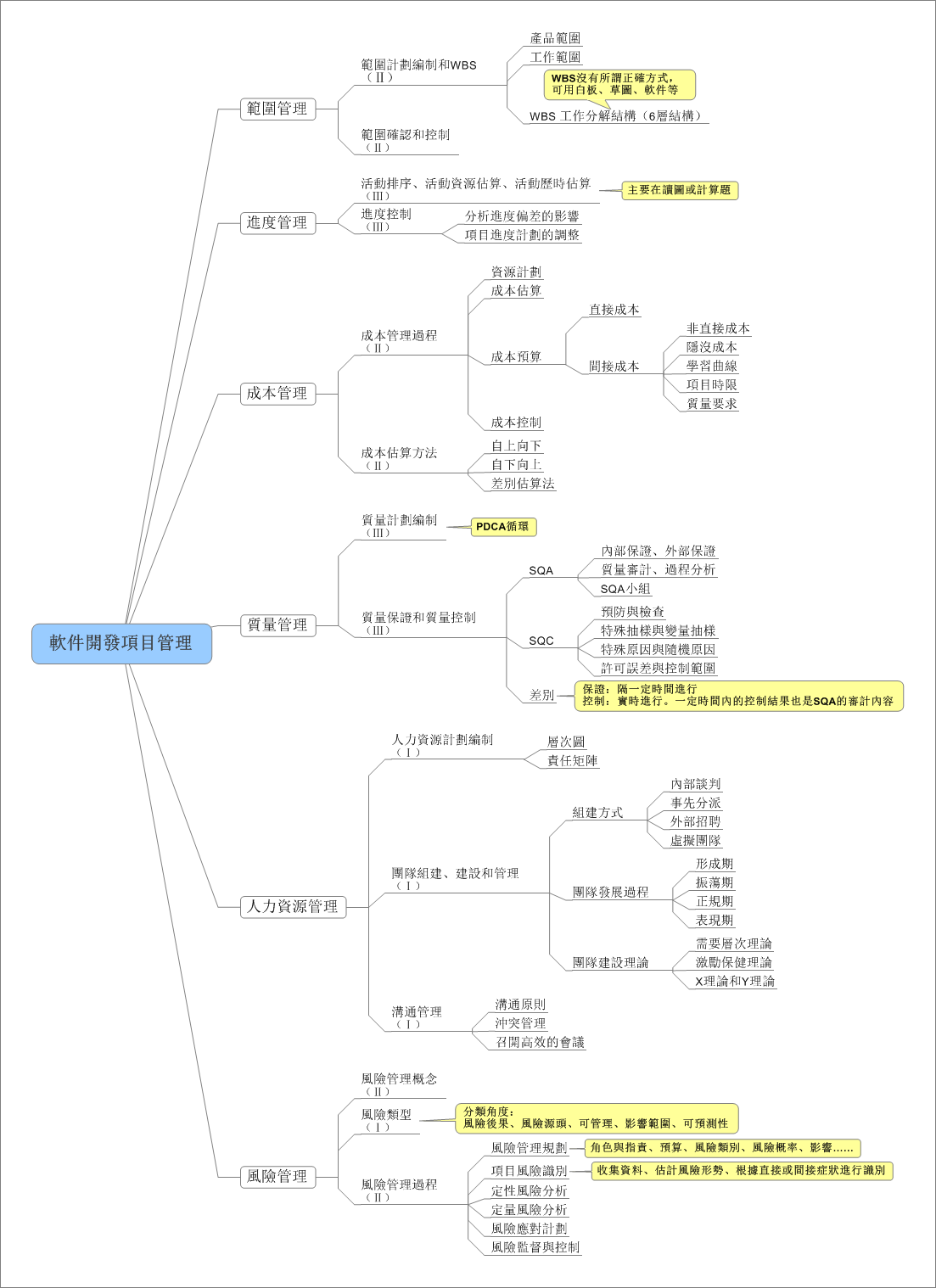
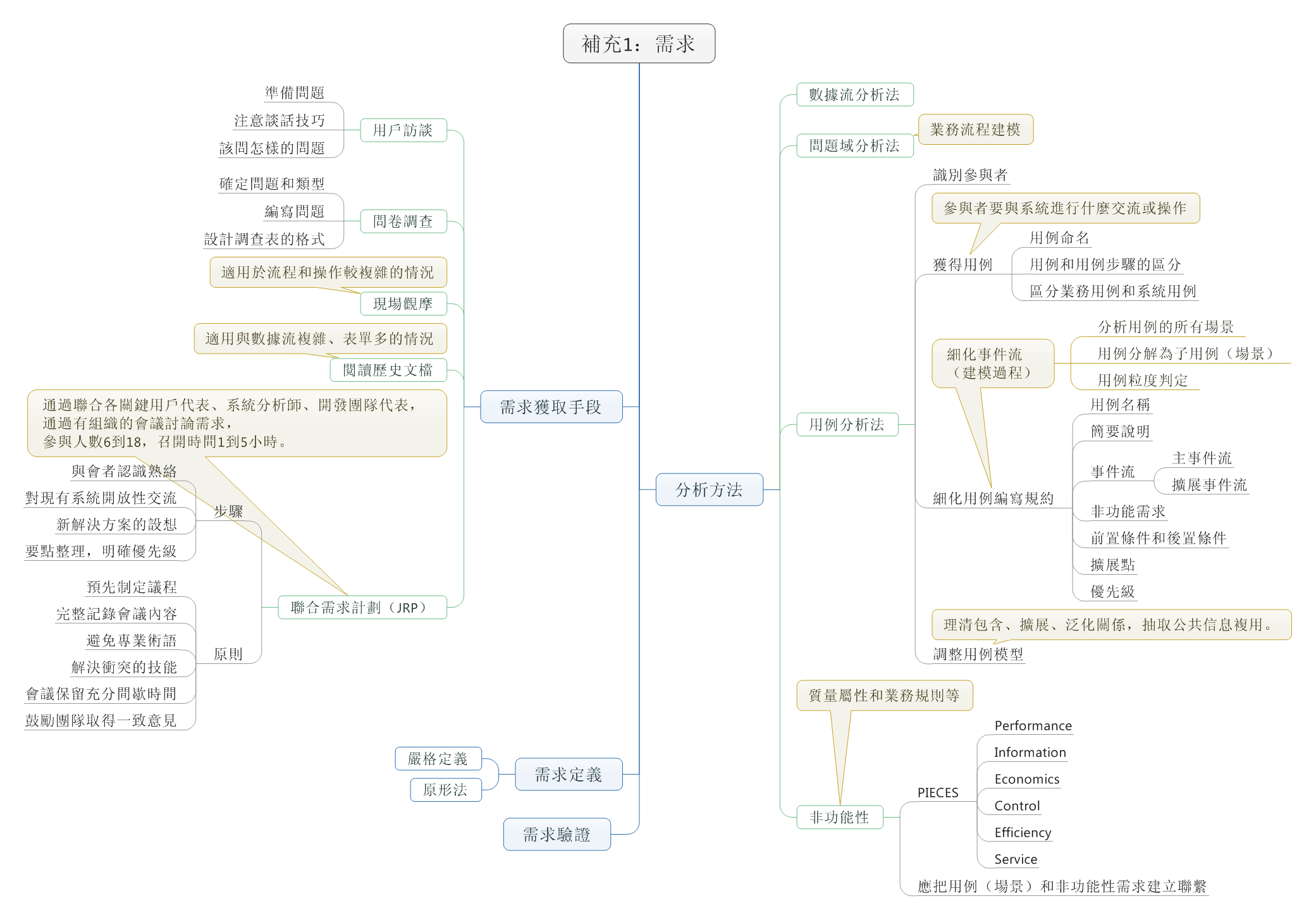
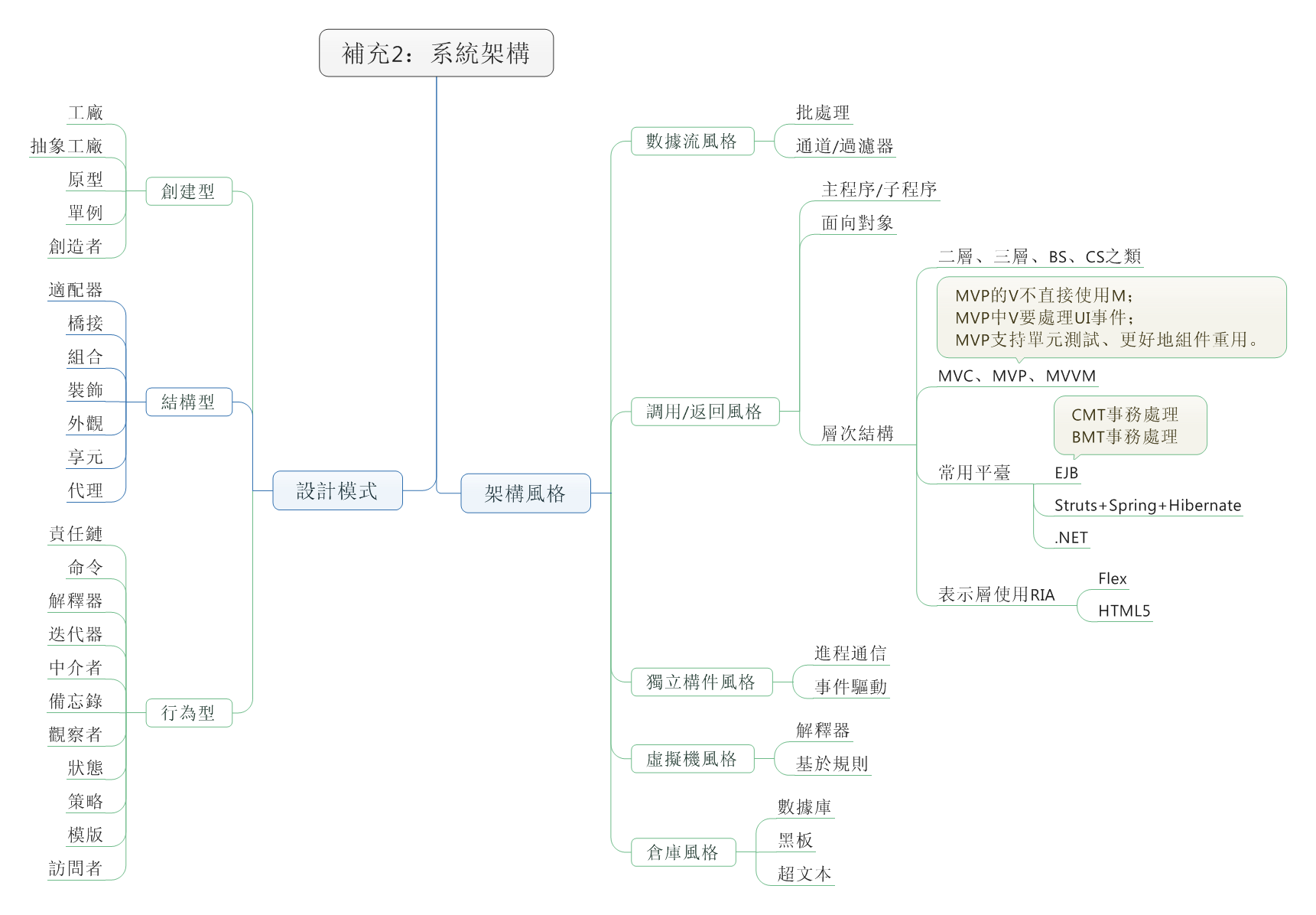
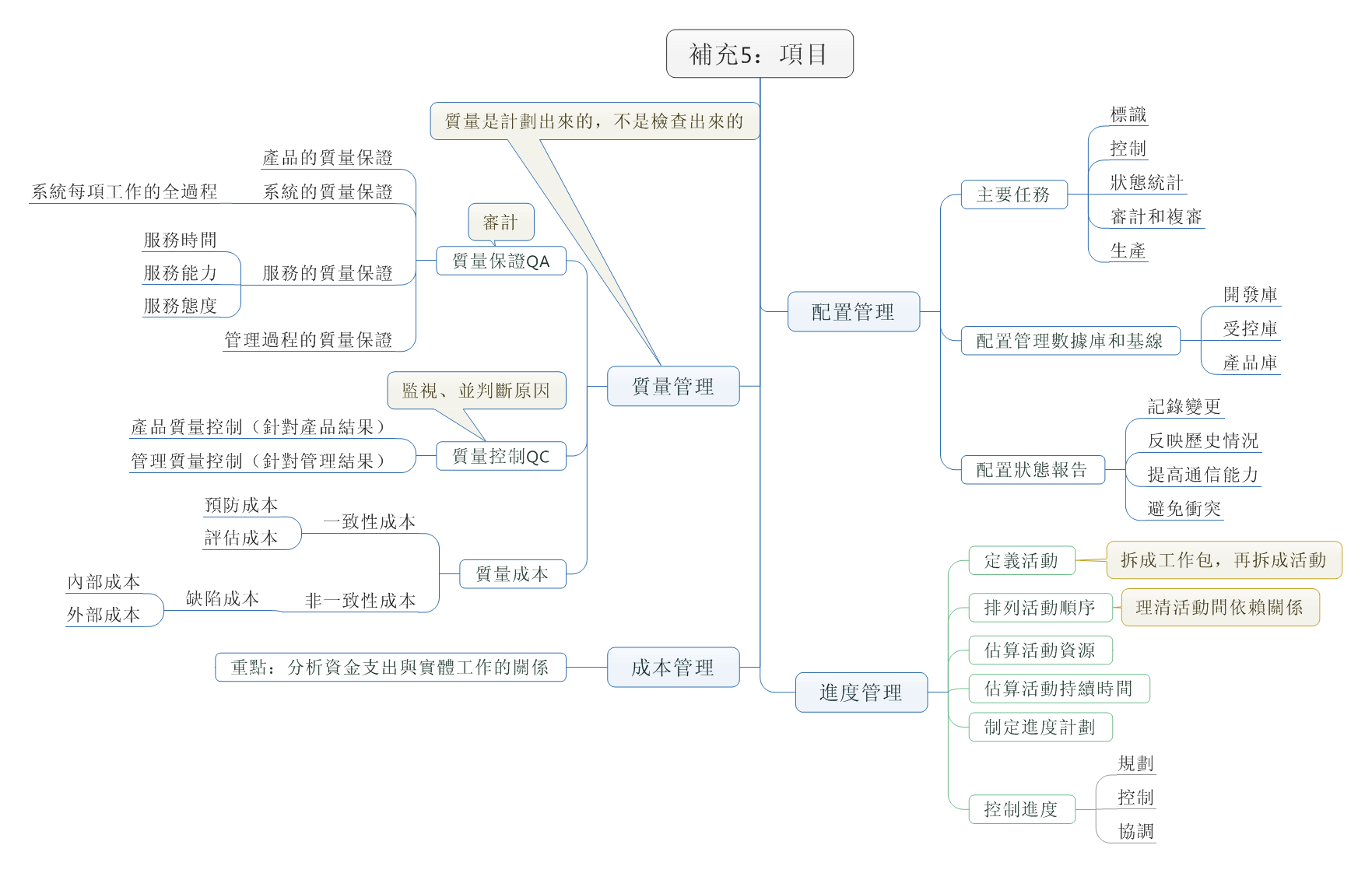
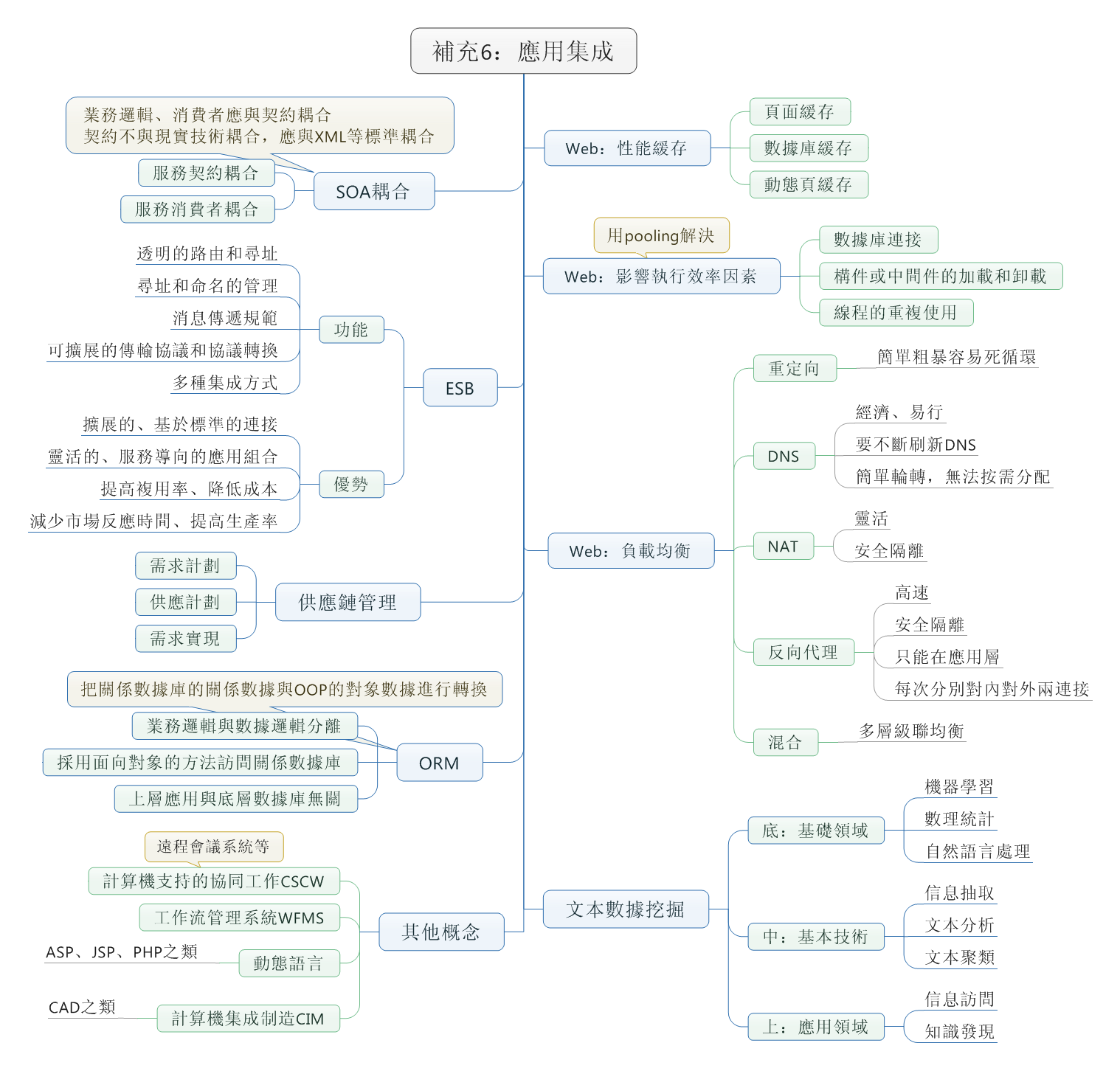
在日常应用中,我们常用结构体或者类来存储一条信息,这种方式很方便,但是不利于数据的传输。例如在网络编程中,我们需要将结构中的数据转化为字节流才能进行传输,我们可以利用memcpy强行将结构化的数据转化为字符串,在接收方以同样的方式转化为来。此法简单易用,但是由于结构化的数据涉及到字符对齐的问题,这种方法会造成额外的数据开销,所以我们最好自己手动对结构化的数据进行编码,当然这种方法也有弊端,虽然在一定程度上节省了传输流量,但结构中的字段很多时,代码量会增大,最好编写工具自动生成一些代码。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENCODE(buf, size, offset, data)\
if ((NULL == buf) || ( == size))\
{\
return -;\
}\
if (offset + sizeof(data) > size)\
{\
return -;\
}\
{\
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t*)buf;\
p=p+offset; \
memcpy(p,&data,sizeof(data)); \
offset = offset + sizeof(data); \
}
#define DECODE(buf, size, offset, data)\
if ((NULL == buf) || ( == size))\
{\
return -;\
}\
if (offset + sizeof(data) > size)\
{\
return -;\
}\
{\
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t*)buf;\
p=p+offset; \
memcpy(&data,p,sizeof(data)); \
offset = offset + sizeof(data); \
}
#define ENCODE_STR(buf, size, offset, data, length)\
if ((NULL == buf) || ( == size) || ( >= length) )\
{\
return -;\
}\
if (offset + length > size)\
{\
return -;\
}\
{\
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t*)buf;\
p=p+offset; \
memcpy(p,data,length); \
offset = offset+ length; \
}
#define DECODE_STR(buf, size, offset, data, length)\
if ((NULL == buf) || ( == size) || ( >= length) )\
{\
return -;\
}\
if (offset + length > size)\
{\
return -;\
}\
{\
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t*)buf;\
p=p+offset; \
memcpy(data,p,length); \
offset = offset+ length; \
}
enum{
enmMaxMsgLength = ,
enmMaxNameLength =
};
class Msg{
int iAge;
char szName[enmMaxNameLength];
double dScore;
public:
Msg()
{
}
Msg(int age,const char* name,double score):iAge(age),dScore(score)
{
strcpy(szName,name);
}
virtual ~Msg(){}
virtual int encode(char *buf)
{
size_t offset = ;
memset(buf,'',enmMaxMsgLength);
ENCODE(buf,enmMaxMsgLength,offset,iAge);
ENCODE_STR(buf,enmMaxMsgLength,offset,szName,enmMaxNameLength);
ENCODE(buf,enmMaxMsgLength,offset,dScore);
return offset;
};
virtual int decode(char *buf,size_t bufSize)
{
size_t offset = ;
DECODE(buf,bufSize,offset,iAge);
DECODE_STR(buf,bufSize,offset,szName,enmMaxNameLength);
DECODE(buf,bufSize,offset,dScore);
return offset;
}
void display()
{
cout<<iAge<<" "<<szName<<" "<<dScore<<endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
size_t offset = ;
char buf[enmMaxMsgLength],*recv = NULL;
Msg msg(,"hwllo world",23.69),msg1;
msg.display();
offset = msg.encode(buf);
cout<<offset<<endl;
cout<<sizeof(Msg)<<endl;
recv = new char[offset];
memcpy(recv,buf,offset);
msg1.decode(recv,offset);
msg1.display();
return ;
}