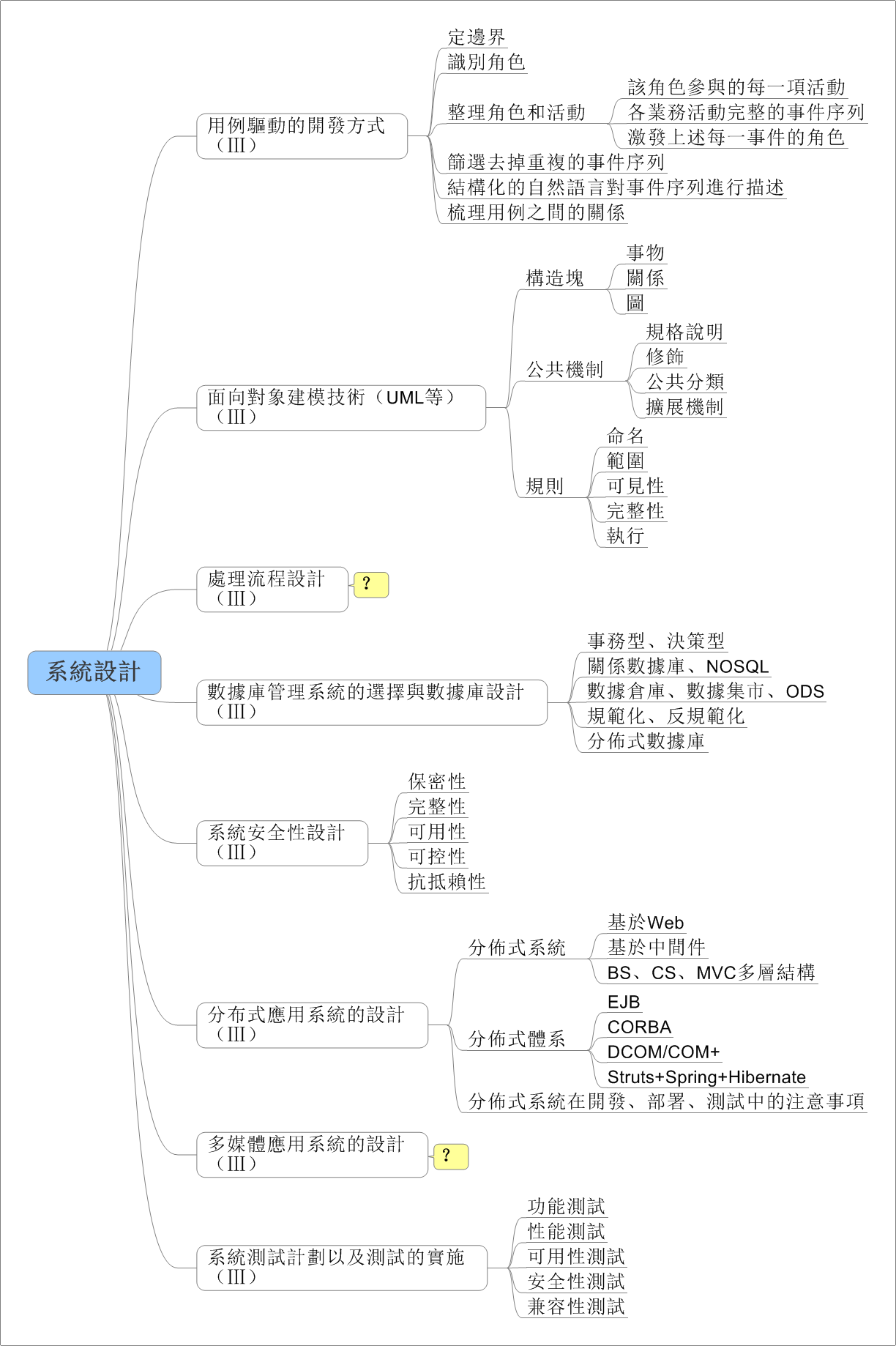
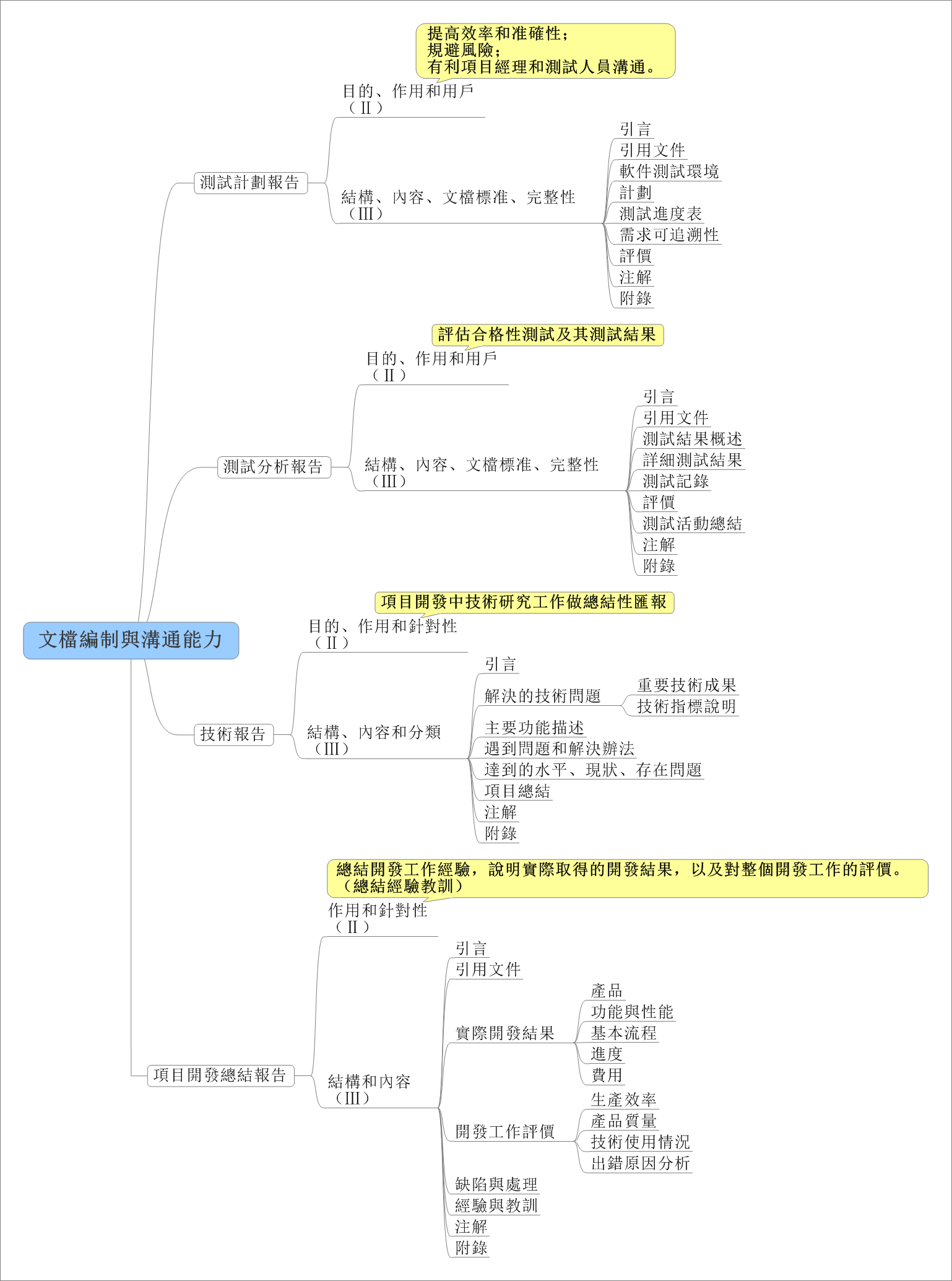
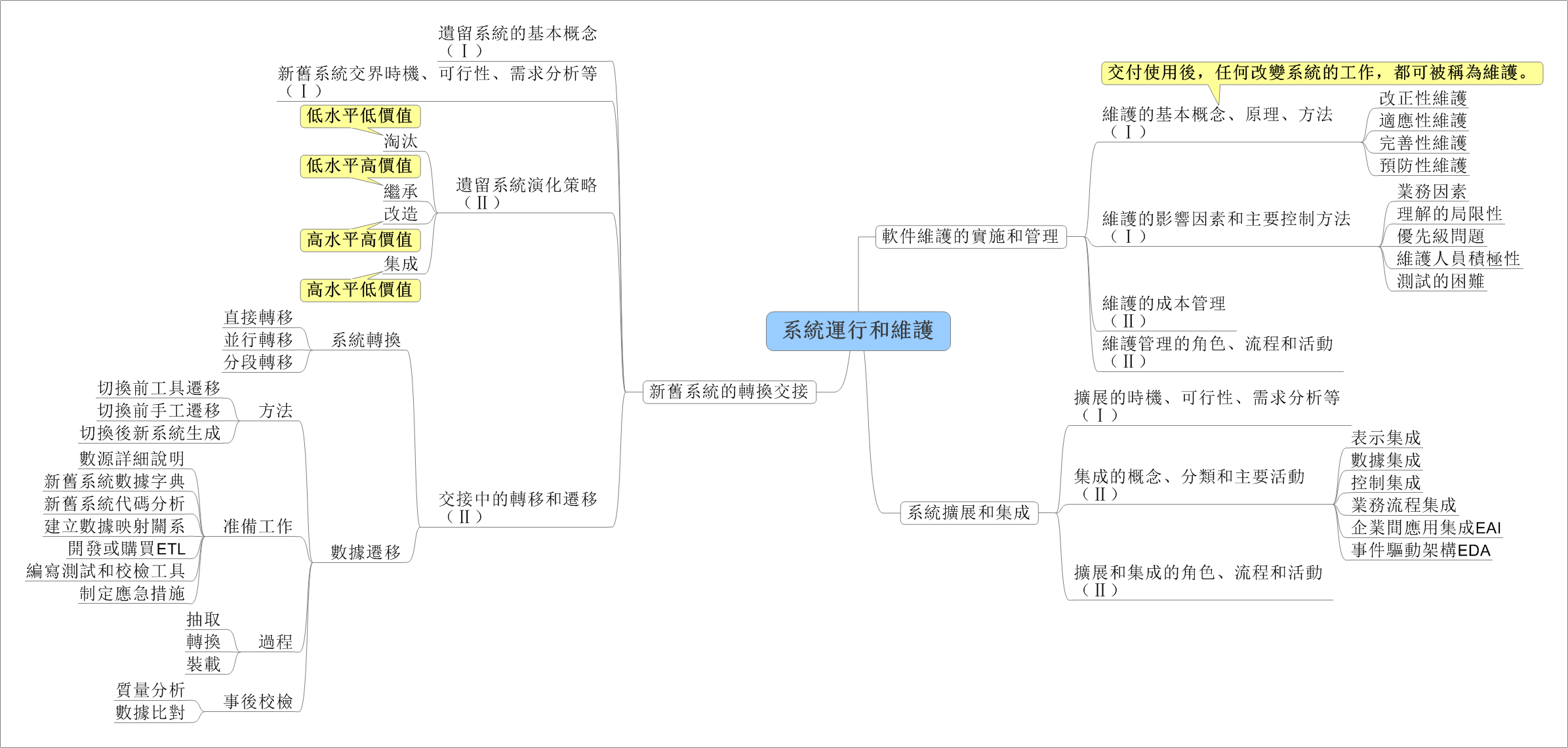
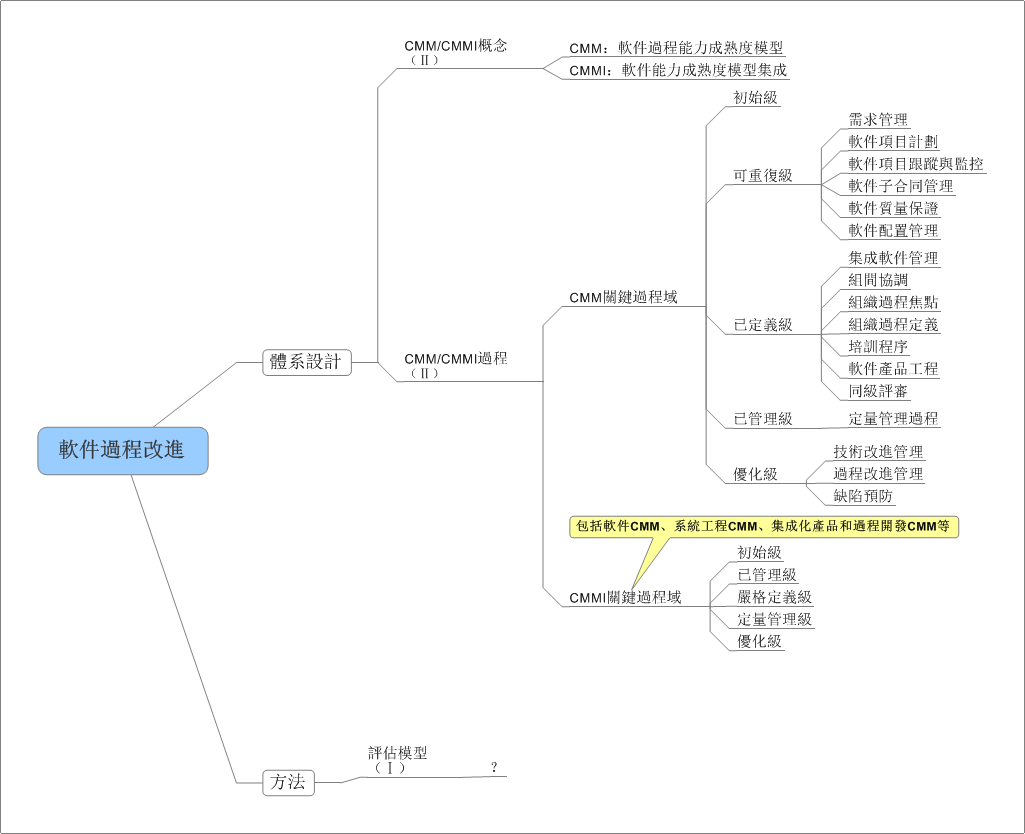
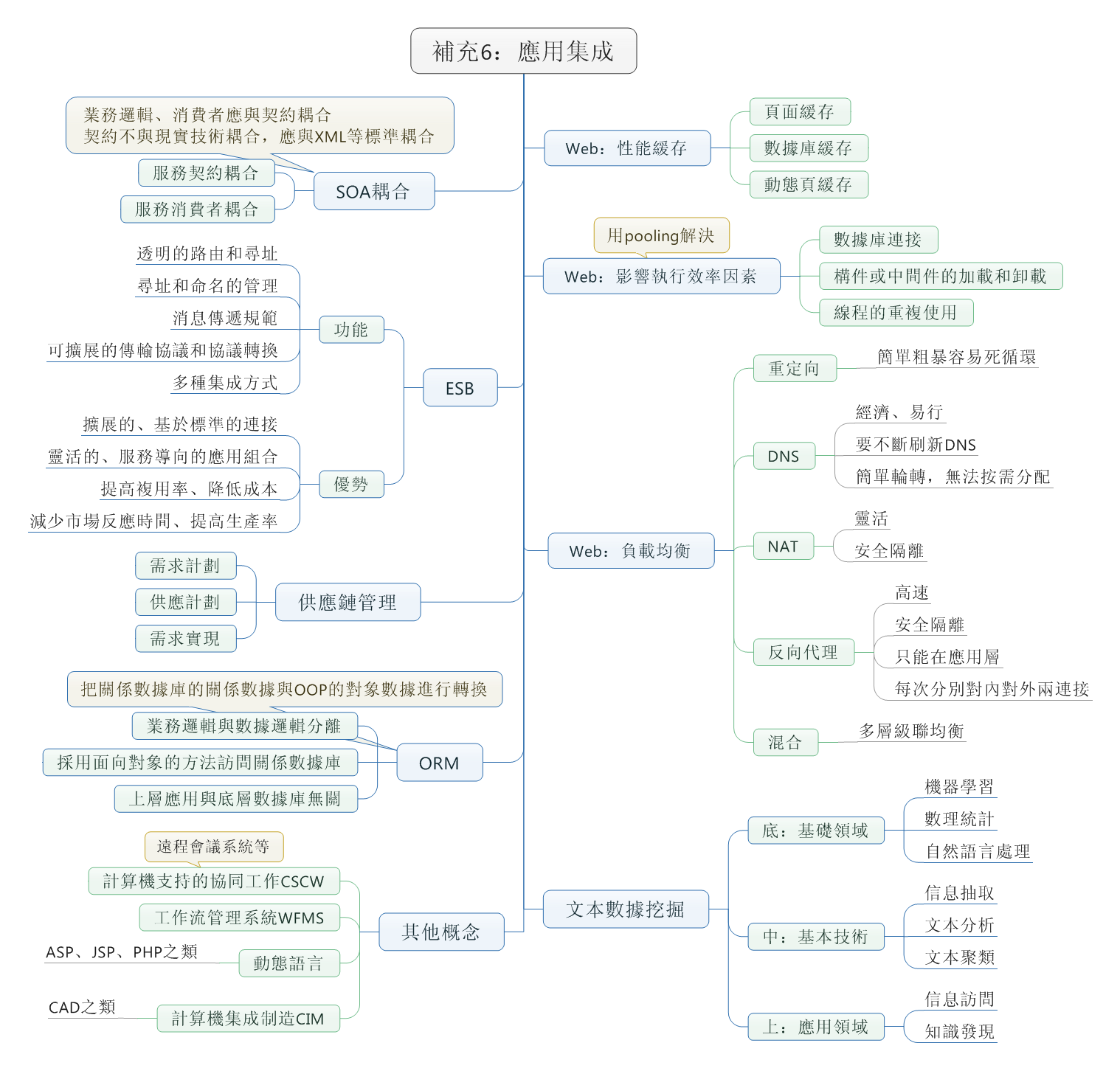
代码摘抄于 Stack Overflow
连接:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12015571/how-to-print-unicode-character-in-c
我一开始的需求是需要在控制台打印进度,用连续的实心正方形来模拟进度,所以就想打印正方形(2588),所以就找到了这个帖子,顺便附上打印实心正方形的代码:
std::cout << "\u2588" << std::endl;以下是一些转换代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int utf8_to_unicode(string utf8_code);
string unicode_to_utf8(int unicode);
int main() {
cout << unicode_to_utf8(36) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(162) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(8364) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(128578) << endl;
cout << unicode_to_utf8(0x24) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(0xa2) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(0x20ac) << '\t';
cout << unicode_to_utf8(0x1f642) << endl;
cout << utf8_to_unicode("$") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("¢") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("€") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("?") << endl;
cout << utf8_to_unicode("\x24") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("\xc2\xa2") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("\xe2\x82\xac") << '\t';
cout << utf8_to_unicode("\xf0\x9f\x99\x82") << endl;
return 0;
}
int utf8_to_unicode(string utf8_code) {
unsigned utf8_size = utf8_code.length();
int unicode = 0;
for (unsigned p = 0; p < utf8_size; ++p) {
int bit_count = (p ? 6 : 8 - utf8_size - (utf8_size == 1 ? 0 : 1)),
shift = (p < utf8_size - 1 ? (6 * (utf8_size - p - 1)) : 0);
for (int k = 0; k < bit_count; ++k)
unicode += ((utf8_code[p] & (1 << k)) << shift);
}
return unicode;
}
string unicode_to_utf8(int unicode) {
string s;
if (unicode >= 0 and unicode <= 0x7f) { // 7F(16) = 127(10)
s = static_cast<char>(unicode);
return s;
} else if (unicode <= 0x7ff) { // 7FF(16) = 2047(10)
unsigned char c1 = 192, c2 = 128;
for (int k = 0; k < 11; ++k) {
if (k < 6) c2 |= (unicode % 64) & (1 << k);
else c1 |= (unicode >> 6) & (1 << (k - 6));
}
s = c1; s += c2;
return s;
} else if (unicode <= 0xffff) { // FFFF(16) = 65535(10)
unsigned char c1 = 224, c2 = 128, c3 = 128;
for (int k = 0; k < 16; ++k) {
if (k < 6) c3 |= (unicode % 64) & (1 << k);
else if (k < 12) c2 |= (unicode >> 6) & (1 << (k - 6));
else c1 |= (unicode >> 12) & (1 << (k - 12));
}
s = c1; s += c2; s += c3;
return s;
} else if (unicode <= 0x1fffff) { // 1FFFFF(16) = 2097151(10)
unsigned char c1 = 240, c2 = 128, c3 = 128, c4 = 128;
for (int k = 0; k < 21; ++k) {
if (k < 6) c4 |= (unicode % 64) & (1 << k);
else if (k < 12) c3 |= (unicode >> 6) & (1 << (k - 6));
else if (k < 18) c2 |= (unicode >> 12) & (1 << (k - 12));
else c1 |= (unicode >> 18) & (1 << (k - 18));
}
s = c1; s += c2; s += c3; s += c4;
return s;
} else if (unicode <= 0x3ffffff) { // 3FFFFFF(16) = 67108863(10)
; // actually, there are no 5-bytes unicodes
} else if (unicode <= 0x7fffffff) { // 7FFFFFFF(16) = 2147483647(10)
; // actually, there are no 6-bytes unicodes
} else ; // incorrect unicode (< 0 or > 2147483647)
return "";
}